others
- 把
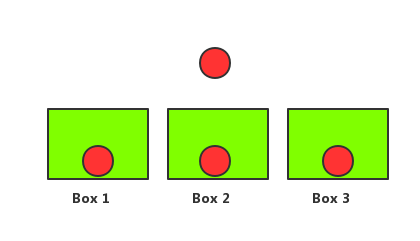
m个球放到n个箱子中,球不可分,箱子可分。每个箱子至少有一个球,共有
种分法。比如下图共有四个球(m=4), 三个箱子(n=3),在保证每个箱子都有球的情况下共有 种放法。
-
现在有
m个球,n个箱子()。现将每个球放进某个箱子中(一个箱子至多放一个球),在保证球互不紧邻的情况下共有多少种放法Y。如下图所示m=2, n=4时,有Y=3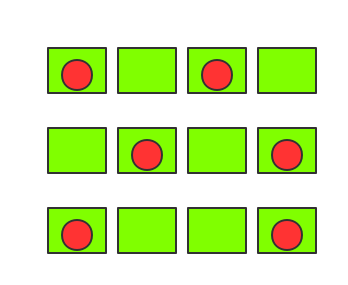
- step 1:
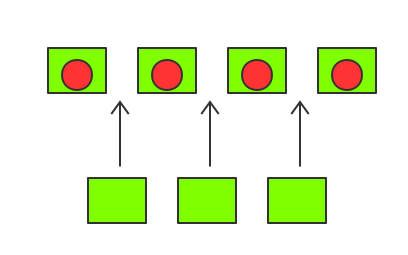
将
m个球放进盒子中后,剩余n-m空箱,为了保证已放球的箱子互相不紧邻,我们需要将剩余的n-m个空箱插入m个球之间的间隙(共有m-1个),并保证每个间隙插入至少一个空箱,如下图所示
-
step2:
step 1中的问题最终转化为将n-m个空箱划分为m-1个组(因此每个组中至少有一个空箱),利用公式Eq.1,我们有种划分方法。 -
step 3: 除了
step 1和step 2中讨论的情况下,我们还有另外两种情况需要考虑,即考虑两侧(或单侧)有空箱的情况,如下图所示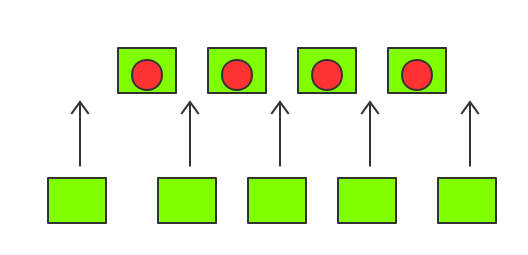
当两侧有空箱时,间隙个数为
m+1;当单侧有空箱时,间隙个数为m - step 1:
将
综上,,其中等式右侧第一,二,三项分别表示序列两侧没有空箱,单侧有空箱,两侧有空箱的情况。
Random sampling
Consider the problem: after doing n times random sampling from n different balls with replacement, what is the probability of that we get different balls in our result (n balls).
If , we have the number of different solutions ,
where
if ,
if ,
…
if ,
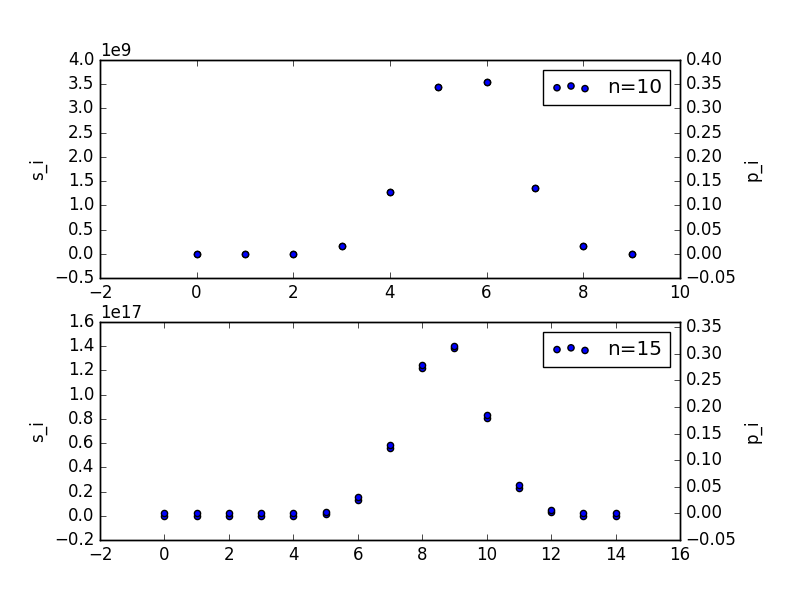
In the following, we show the scatter plots of and in cases and , the code of computing and can be found in github.
It worth noting that
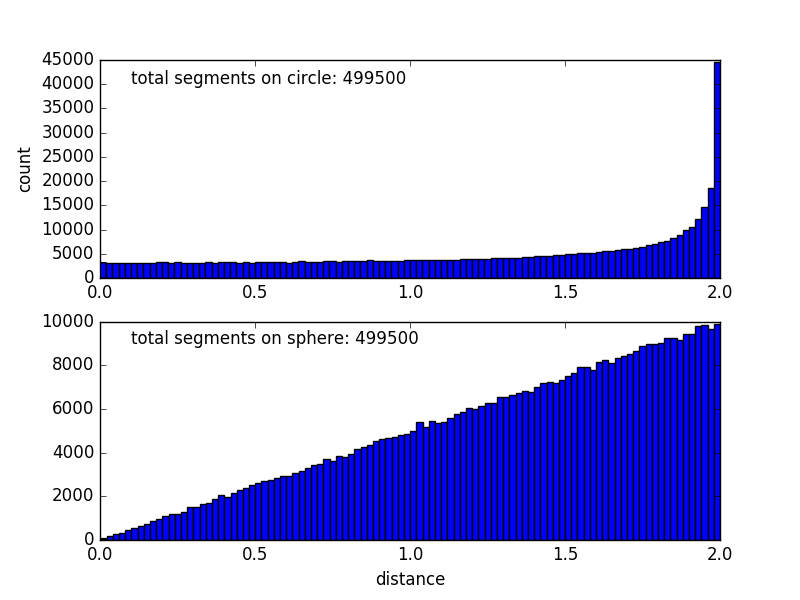
Distances distribution on circle/sphere
We compute the distribution of the distances of pairs of points on on a circle/sphere with radius , the data points are uniformly randomly sampled as the following code showing:
def circle_points(n_samples):
"""
inputs
------
n_samples: int
return
------
u: 2D np.ndarray with shape=[n_samples, 2]
"""
theta = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=2 * np.pi, size=(n_samples, 1))
u = np.concatenate([np.cos(theta), np.sin(theta)], axis=1)
return u
def sphere_points(n_samples):
"""
inputs
------
n_samples: int
return
------
u: 2D np.ndarray with shape=[n_samples, 3]
"""
theta = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=2 * np.pi, size=(n_samples, 1))
z = np.random.uniform(low=-1.0, high=1.0, size=(n_samples, 1))
x = np.sqrt(1 - z**2) * np.cos(theta)
y = np.sqrt(1 - z**2) * np.sin(theta)
u = np.concatenate([x, y, z], axis=1)
return u
def distance(x, y):
"""
inputs
------
x: 2D np.ndarray with shape=[n1, dim]
y: 2D np.ndarray with shape=[n2, dim]
return
------
dist: 2D np.ndarray with shape=[n1, n2],
dist[i, j] = distance(x[i], y[j])
"""
assert len(x.shape) == len(y.shape) == 2
assert x.shape[1] == y.shape[1]
x = x[:, np.newaxis, :]
y = y[np.newaxis, :, :]
z = np.square(x - y)
dist = np.sqrt(np.sum(z, axis=-1))
return dist